If you tell an astronaut that there is a Space Spider on the International Space Station, the last thing you'll hear them do is scream. First off, no one would hear them anyway, and secondly, the Space Spider makes their engineering tasks so easy it's scary. Unfortunately, Artec, which designed the handheld 3D scanner, wouldn't tell us exactly how the space station uses the metrological device(alien autopsies perhaps?). Judging by how it's used on terra firma, though, the possibilities are endless. We recently asked Artec marketing manager Daniela Carr to enlighten us on some of those possibilities, and some of the features that made the 3D scanner a 2016 NED Innovation Award nominee.
How does the Space Spider work?
The Artec Space Spider is a structured light 3D scanner. You point and move it around an object like you might a video camera, and record all the details on every side of the object. The scanner works by projecting a grid pattern on the object and calculating its deformation. Once you have captured the object, you need to do some quick post processing of the data and create the final 3D model in the Artec Studio software.The result is a highly precise 3D replica of the object you scanned.
The Space Spider was developed for the International Space Station. Can you tell us what makes it so useful in space and how it's used?
It took just under a year for us to evolve Spider into Space Spider. The Space Spider features higher grade electronics than Spider and an internal smart temperature system which automatically regulate its core temperature. This allows the scanner to reach its optimal working temperature in 3 min, as opposed to the 30-min time of our original Spider. The system maintains this temperature during even the longest scanning sessions, meaning that maximum accuracy is achieved in minimum time, and ensures that the scanner can provide maximum precision and repeatability in data capture regardless of any small fluctuations in ambient temperature. Additionally, the electronics were specially reinforced to create a robust device which can be relied on to be used for long periods in a remote location, such as in space.
As for how it is being used on the space station, we would love to be able to share this, but unfortunately we are not able to.
The Artec Space Spider was developed for use on the International Space Station.
photo credit: NASA
What are the most important features that give the 3D renderings such detail and clarity?
Space Spider provides 3D point accuracy of up to 0.05 mm and 3D resolution of up to 0.1 mm.
Why would someone bundle this with the Artec Eva?
Eva is great for scanning medium to large objects/ areas because it scans quickly and accurately. If you want to scan small objects or intricate areas of large objects which need higher precision, for metrological applications for example, then you need to use Space Spider.
If you are using Eva and Space Spider together, then you will need to align the scans manually. If you are an Artec Studio user, this is not at all difficult, but does obviously take a little longer than making a model from data captured by only one scanner.
Why is this a good investment for a company?
3D scanning is much faster than using traditional methods such as casting. Also, once you scan something, you will have a 3D replica to use as many times as you like.
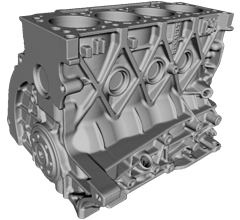
An engine digitally created with the Eva and Space Spider
The main advantage of all Artec 3D scanners is that they save time and physical material. Space Spider is especially useful for metrological applications because, unlike usual metrological tools which require a lot of careful and time-consuming preparation, it is in optimal readiness after only 3 min. It's currently used by major companies in the aerospace, defense and the automotive industries in many ways.
It's used for rapid prototyping. There it really speeds up the process of scanning models of objects to quickly get a CAD drawing. In product design and manufacture, it scans small body parts to create comfortably fitting objects, such as earbuds. It's also used to reverse engineer. You can scan older technology without documentation to create CAD files which can then be used to create modifications or replacement parts. One other use is in quality control, because you're able to accurately measure how an object has deformed over time.
How can it be used to improve people’s lives on a larger scale?
Artec scanners are also great for any kind of customization. So in the future this will spread a lot more to the consumer market. For example, you may want a customized bicycle saddle for extra comfort.
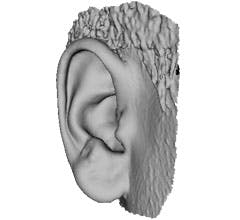
A scanned ear can help design more comfortable cochlear implants and ear buds.
You can go to a 3D scanning and printing center, where they will scan you, create the saddle design which follows the shape of your body exactly, and then print it.
In healthcare, it can be used for scanning small body parts, such as ears in order to create a prosthetic that is an exact match. This is a much quicker and more pleasant process for the patient than the traditional plaster cast process.
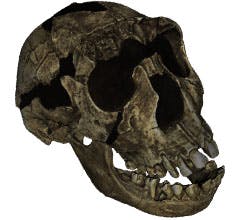
The two pieces of Turkana Boy's skull were scanned by the Space Spider to digitally capture every detail of the the 1.6 million-year old Homo Erectus.
About the Author
John Hitch
Editor, Fleet Maintenance
John Hitch, based out of Cleveland, Ohio, is the editor of Fleet Maintenance, a B2B magazine that addresses the service needs for all commercial vehicle makes and models (Classes 1-8), ranging from shop management strategies to the latest tools to enhance uptime.
He previously wrote about equipment and fleet operations and management for FleetOwner, and prior to that, manufacturing and advanced technology for IndustryWeek and New Equipment Digest. He is an award-winning journalist and former sonar technician aboard a nuclear-powered submarine where he served honorably aboard the fast-attack submarine USS Oklahoma City (SSN-723).