Just how modern is your supply chain, and where do you think it will be in the next decade?
This is essentially what the 2016 MHI Annual Industry Report, titled Accelerating Change: How Innovation is driving digital “always-on” supply chains, asked of 900 industry insiders, including manufacturers, distributors, service providers, and others. More than half were senior executives, general managers, or department heads.
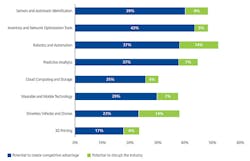
Of the 900 people surveyed, 83% targeted one of the following eight specific technologies to give their supply chain a competitive edge in the next decade. Here’s a primer on each, and how important each is predicted to be, according to those surveyed.
1) Predictive Analytics
It’s Moneyball for your supply chain. A predictive analytics solution models all the behavioral data it can collect, from inventory to machinery life cycles, identifies the patterns, and then prognosticates when the widgets would run out or a conveyor could break down.
Using Tableau’s analytics software suite, along with sensitivity analysis, regression analysis and Monte Carlo simulation, an aerospace company reduced inventory by $100 million and average lead times by 35%.
Predictive analytics can help you reduce inventory and lead times.
Screengrab: Tableau
| Competitive Advantage: 37% Disruption: 7% Current Adoption Rate: 22% Future Adoption Rate (6-10 years): 80% |
2) Robotics & Automation:
Thanks to improved sensors and safety guidelines, robots aren’t locked away behind safety fences, programmed only to do one rote task. The dawn of collaborative robots is upon us, and they’re getting safer and more versatile every day.
What’s one of the biggest future improvements?
“We’re going to see robots with vision,” says Scott Melton, regional manager of FANUC America West. “3D vision for bin picking, for handling mixed products, a technology that allows you to sort product by size, allowing mixed products to come into the robot zone. This allows product to come in randomly or as needed.”
An integrated Fanuc IRvision system tells dual Fanuc LR Mate 200iD robots which paper cups need to be picked and replaced.
Photo: Fanuc America Corp
Seegrid has already implemented stereoscopic vision in its Vision Guided Vehicles, so they can “see” like humans and weave around the factory floor with more confidence. When this becomes more commonplace with picking robots, as Melton predicts, there’s no telling how productive your supply chain can be (unless you use that predictive software).
| Competitive Advantage: 37% Disruption: 14% Current Adoption Rate: 35% Future Adoption Rate (6-10 years): 74% |
3) Sensors & Automatic Identification
In 2007, there were about 10 million devices embedded with sensors; in 2030, there will be 10 trillion. This means if you don’t already know a little about the Internet of Things (a.ka. Industry 4.0), you have a lot of catching up to do. (Don’t worry. We have you covered.)
IoT isn’t some just some esoteric philosophy about improving the world by connecting it. Even if you make artisanal cheeses out of your garage, the IoT can help you. You can use a smart fridge to check your product’s temperature and keep track of inventory via a smartphone barcode scanner.
But what if you aren’t a fancy pants cheese monger? How can the IoT help your supply chain?
Using indoor GPS, forklift drivers can accurately receive location and direction information for pallets, and in turn, managers can get real-time data on the forklift’s location and production. The report says that one customer who used this technology experienced a 30% increase in pallets moved per hour.
| Competitive Advantage: 39% Disruption: 8% Current Adoption Rate: 44% Future Adoption Rate (6-10 years): 87% |
4) Wearables & Mobile Technology
Amazon's drone delivery system
Photo: Amazon.com
These are just a few reasons why the report pegs this as having the highest potential for disruption (tied with robotics).
| Competitive Advantage: 23% Disruption: 14% Current Adoption Rate: 9% Future Adoption Rate (6-10 years): 50% |
6) Inventory and network optimization tools
The already high adoption rate of this technology could double in as early as six years, insiders say. It’s not a bold a prediction, considering that every company needs to increase efficiency, lower fuel costs, and improve inventory control. These are just a few things an inventory and optimization platform can do.
And this spans the entire length of the supply chain. On the transportation management end, implementing a product such as Manhattan Associates’ Driver&Load could improve on-time pickup, enhance customer services, and decrease deadhead miles.
| Competitive Advantage: 43% Disruption: 5% Current Adoption Rate: 43% Future Adoption Rate (6-10 years): 90% |
7) Cloud computing and storage
Not many (4%) believe the cloud will cause supply chain disruption, but by 2026, 86% expect to employ the cloud in some fashion.
And that will at the very least improve communication within a logistics network.
“When information is no longer maintained in siloed systems that are accessible to one department or one partner, multiple departments can use the information to improve performance and planning,” says Justin Stone, account manager at Deposco. “Cloud-based applications also enable the use of mobile technology, which improves efficiency and real-time data collection.”
| Competitive Advantage: 25% Disruption: 4% Current Adoption Rate: 45% Future Adoption Rate (6-10 years): 86% |
8) 3D Printing
We love writing about the 3D printing industry. Every day it gives us some example of how it can be used creatively to solve health problems or turn your cat into a gladiator.
The technology’s use in the supply chain is a bit more understated, but can lower tooling, material, and processing costs. It’s a fairly simple premise: You can carry less inventory, because if you run out, just print some more.
It’s science, not magic, so there are some considerable limitations based on size and materials. But the amount of workable materials has expanded from simple ABS plastic to thermoplastics, titanium and more.
There’s also a growing trend of outsourcing parts to a company such as 3D Systems' Quickparts.
ProX DMP 320 offers fast build turnaround times in demanding 24/7 production environments.
Photo: 3D Systems
The report concludes that “as 3D printing approaches a breakeven point, manufacturers are likely to begin adopting it as standard practice.”
| Competitive Advantage: 17% Disruption: 6% Current Adoption Rate: 14% Future Adoption Rate (6-10 years): 48% |
The Top Eight Technologies for Supply Chain
Source: MHI
Let us know in the comment section how many of these your supply chain implementing, and which you think is the most disruptive.